Invitro Cell viability and proliferation assay are used to deduce limiting cytotoxic concentration of any sample. Followed by this Scratch Assay is performed to determine the effect of proliferative concentration of the sample in induction of cell migration and wound healing. Invitro model for wound healing are used to study re-epithelization, contraction and angiogenesis (Phan).
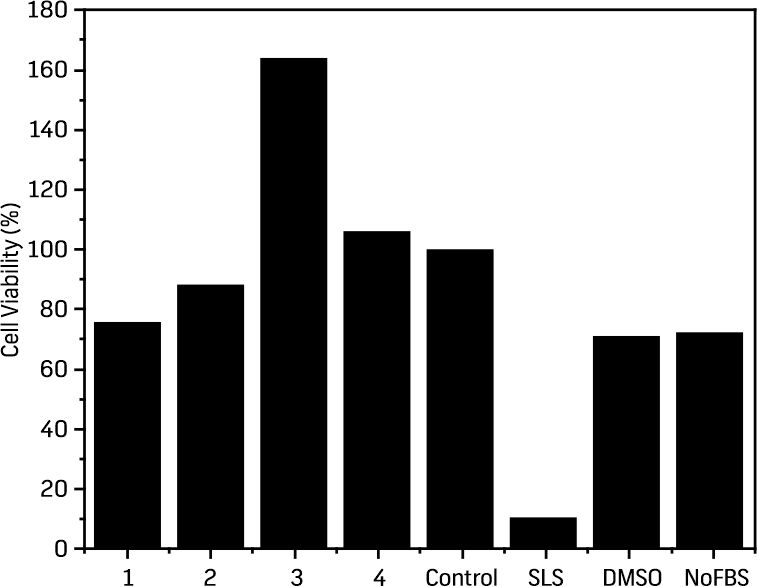
D2PRO was tested for cell proliferation ability on 3T3 mice fibroblast cell lines. The cells were in serum deprived medium supplemented with various concentration of D2PRO (Fig 1). The results showed that up to 1 mg/ ml of D2PRO the oil showed no toxic effects in comparison to cells treated with media without serum. With serum the cells showed 100% proliferation which is considered as cell control.
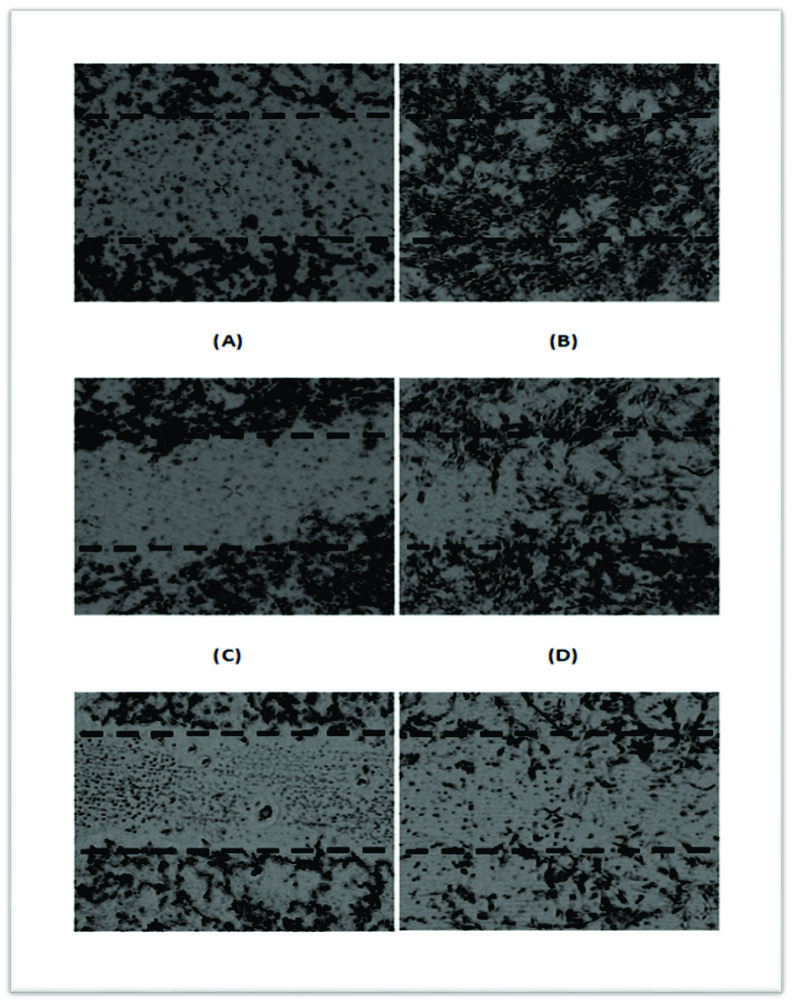
In-vitro tests – One such methods is wound healing assay, wherein a wound is created on monolayer of cells, and after treatment images are captured at regular intervals and compared to quantify the migration, cell-matrix or cell-cell interactions. It is typically reliable, inexpensive, quick and mimics migration during healing of wounds invivo (Rodriguez).
Wound healing ability of D2PRO was assessed using Scratch Test. However, complete wound healing of 98% was observed in concentration 0.5mg/ml which also co-relates to highest cell proliferation in viability test (64.00% more than media control containing 10% FBS).
The sample was screened for free radical scavenging/antioxidant ability by DPPH assay. at 0.5 mg/ml of the sample, 15% antioxidant activity was found. Presence of phytocompounds such as tannins, saponins, terpenoids, cardiac glycosides, phenolics and flavonoids may be resulted into antioxidant activity of D2PRO
D2PRO Oil sample was tested for antimicrobial activity against S. aureus and P. aeruginosa using Time Kill Method. The antimicrobial activity was calculated in percent kill for 0.5mg/ml of the oil sample tested. Even at such less concentration percent kill was found to be 6% and 15% after 4 and 8 hours respectively against S. aureus. Slightly higher kill was observed towards P. aeruginosa which was 11% and 20% after 4 and 8 hours respectively.